To measure for Inserts, Plastic Caps and Ferrules, follow these key steps:
1. Consider Shape and Fit of Tube
Identify if the tube is round, square, rectangular, or another shape. Measure all relevant dimensions (e.g., width and height for square tubes) to ensure compatibility with fittings. Also, look for any tapers, dents, or manufacturing imperfections that might affect fit. Understanding the tube’s shape and potential imperfections helps avoid issues during installation or use.


2. Measure the External Tube Diamater
Use a caliper for precise measurements. Ensure the caliper jaws are square to the tube to avoid errors. Measure at several points along the tube’s length to detect inconsistencies. This is especially important for tubes that might be slightly oval or irregular, as these variations can impact fitting selection.


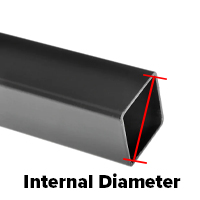
3. Measure the Internal Tube Diamater
For hollow tubes, use calipers to measure the inside diameter. Carefully expand the caliper inside the tube until it touches the inner walls. Rotate slightly to ensure a consistent measurement and check at multiple points. This step helps determine the correct insert or cap size, ensuring a secure fit.

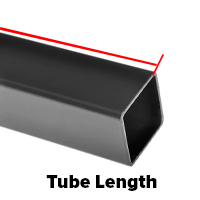
4. Measure Tube Length
Lay the tube on a flat, stable surface to prevent any bending during measurement. Use a tape measure or ruler aligned perfectly straight with the tube, measuring from end to end. Measure twice to confirm accuracy, especially if the tube will be cut to a specific size for fittings or structural applications.

5. Measure the Tube Wall Thickness
Next, measure the tube wall thickness. This can be calculated by subtracting the internal diameter from the external diameter of the tube (Tube wall thickness = External Diameter – Internal Diameter). Understanding this measurement is important for selecting the right insert or cap, especially when dealing with varying wall thicknesses.
Our comprehensive range of round, square, and rectangular inserts is specifically designed to fit flush with your hollow tubes. Each insert features side fins that retract upon insertion, ensuring a snug and secure fit. For commonly used sizes, we offer plastic inserts that accommodate different tube wall thicknesses, providing versatility for various applications.
Tube wall thickness is often referred to as a "gauge." Below is a table that correlates tube wall thickness with the corresponding gauge number:
| Tube Wall Thickness (mm) | Gauge |
|---|---|
| 0.91 | 20 |
| 1.01 | 19 |
| 1.21 | 18 |
| 1.42 | 17 |
| 1.62 | 16 |
| 1.82 | 15 |
| 2.03 | 14 |
| 2.33 | 13 |
| 2.64 | 12 |
| 2.94 | 11 |
| 3.25 | 10 |
| 3.65 | 9 |
| 4.06 | 8 |
| 4.47 | 7 |
| 4.87 | 6 |
| 5.38 | 5 |
| 5.89 | 4 |
Conclusion
With accurate measurements of your external tube diameter and wall thickness, we can provide you with the appropriate plastic inserts and caps to meet your needs.
The same measurement principles apply to our rod and wire end tips, plastic ferrules, rubber ferrules, and rubber bungs. For bolt and nut caps, measurements are based on the thread diameter, which corresponds to a standard hexagonal head size. Threaded tube inserts should be measured in the same manner as blanking plugs, focusing on external tube diameter and tube wall thickness.
We offer a wide range of imperial and metric sizes for tube fittings. If you're unsure of your measurements, simply provide the closest dimensions you can, and we'll recommend the best available options.
If you'd like to test our products, please feel free to contact us for a free sample of our tube fittings. We're happy to assist you in finding the perfect fit for your application.





